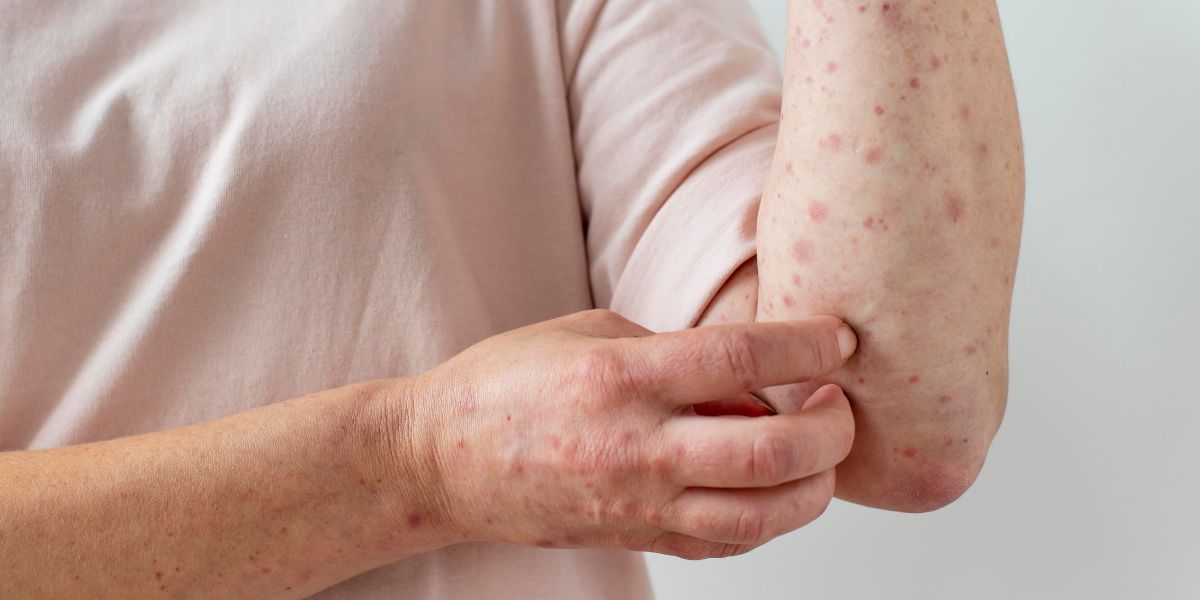
Kapanlagi.com - Who doesn't know about chickenpox? This disease is often considered trivial, especially by children. However, don't be mistaken! Chickenpox, or varicella, caused by the Varicella zoster virus, can pose a serious threat, especially to adults. Characterized by itchy red rashes filled with fluid, chickenpox may seem mild, but it can be dangerous for those with weakened immune systems.
Chickenpox can spread rapidly through the air, especially when the infected person coughs, sneezes, or even shares personal items. For those who have never been infected or have not been vaccinated, the risk of contracting the virus and experiencing more severe symptoms increases.
The symptoms of chickenpox do not appear instantly after exposure to the virus. They develop gradually, making it important for us to recognize the early signs. By doing so, we can take appropriate preventive and treatment measures to avoid getting caught in a bigger problem. This article will delve deeper into the symptoms, spread, complications, treatment, and prevention of chickenpox.
1. How Does Chickenpox Spread?
Chickenpox is a highly contagious disease that can easily spread from one individual to another. Its transmission occurs in several ways, including:
- Through the air – The virus can be transmitted through droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes.
- Direct contact with blisters – Touching the fluid from a ruptured chickenpox blister can cause transmission.
- Personal items of the infected – The virus can stick to items used by the infected person, such as clothing or towels, potentially spreading to others.
According to experts, a person can transmit chickenpox from two days before the rash appears until all the blisters have dried and turned into scabs. Therefore, if there is a family member or coworker who has chickenpox, it is advisable to maintain distance to reduce the risk of transmission.
2. Symptoms of Chickenpox in Children and Adults
The symptoms of chickenpox in children and adults have several similarities, but in adults, they are usually more severe. Here are some common symptoms:
- Low to high fever
- Body aches and headaches
- Loss of appetite
- Fatigue and discomfort
- Appearance of red rashes that develop into fluid-filled blisters
The blisters that appear usually start from the face, chest, or back, then spread across the body. In children, these symptoms tend to be milder and resolve quickly. However, in adults, the symptoms can be more intense, last longer, and carry a risk of serious complications.
3. Complications That May Arise from Chickenpox
Although chickenpox is classified as a self-limiting disease, there are risks of complications that need to be watched for, especially in individuals with weakened immune systems. Some possible complications include:
- Skin infections – If chickenpox blisters are scratched and become infected with bacteria, it can lead to more serious skin infections.
- Pneumonia – Viral infections can spread to the lungs and cause inflammation.
- Brain inflammation (encephalitis) – Although rare, chickenpox can also cause dangerous inflammation in the brain.
- Reye's syndrome – This condition is more common in children who take aspirin while having chickenpox.
In pregnant women, chickenpox can pose a risk of the baby being born with low birth weight or congenital defects. Therefore, it is important to consult a doctor immediately if experiencing concerning symptoms.
4. Treatment and Management of Chickenpox
Chickenpox generally heals on its own within 5-10 days. However, there are several steps that can be taken to alleviate symptoms and speed up recovery:
- Increase water intake to prevent dehydration.
- Use calamine lotion to reduce itching on the skin.
- Avoid scratching the rash to prevent secondary infections.
- Take pain relievers such as paracetamol if experiencing fever or body aches.
- Wear loose and comfortable clothing to avoid skin irritation.
In more severe cases, a doctor may prescribe antivirals such as acyclovir to reduce the severity of the illness and prevent complications.
5. Effective Prevention of Chickenpox
The best way to prevent chickenpox is through vaccination. The varicella vaccine is recommended for both children and adults who have never had chickenpox before. This vaccine is usually given in two doses:
- First dose: When the child is 12-15 months old.
- Second dose: When the child is 2-4 years old.
For adults who have never had chickenpox, vaccination can be done twice with a minimum interval of 28 days. In addition to vaccination, several other steps can also be taken to reduce the risk of infection, such as maintaining hand hygiene, avoiding contact with infected individuals, and boosting immunity through a healthy lifestyle.
6. People Also Ask
1. Can someone get chickenpox more than once?
It is very rare, but it is possible for someone to get chickenpox more than once if their immune system is very weak.
2. What should be done if chickenpox affects the eyes?
See a doctor immediately if a chickenpox rash appears around or in the eyes as it can risk causing vision problems.
3. How long can chickenpox be contagious?
Chickenpox can be contagious from two days before the rash appears until all the blisters have dried and formed scabs.
(kpl/rmt)
Disclaimer: This translation from Bahasa Indonesia to English has been generated by Artificial Intelligence.