How to Cook Rendang for Tender Meat and Unbroken Coconut Milk, Tips for Perfectly Cooked Serving
In this article, we will discuss the steps to cook rendang so that the meat is tender and the coconut milk remains intact.
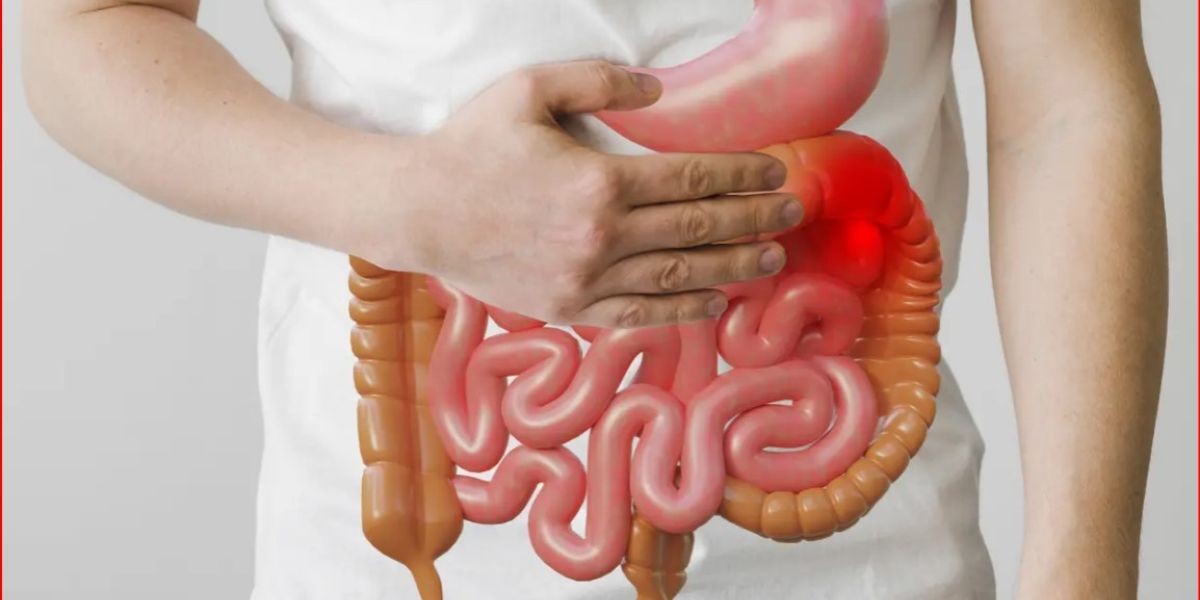
Kapanlagi.com - In the past, colorectal cancer was more often associated with older age, but now this disease is beginning to target younger people. The spike in cases among the productive generation raises serious concerns in the medical world. Changes in lifestyle and modern eating habits have become one of the main triggers that we must be aware of.
One of the biggest challenges of colorectal cancer is its ability to develop without symptoms in the early stages. As a result, many people only realize there is a problem when the disease has already reached an advanced stage. In fact, early detection through screening can be a lifesaver. Unfortunately, many still ignore the importance of regular check-ups.
Colorectal cancer often begins from polyps in the large intestine or rectum, which if not treated, can become malignant. Without proper treatment, this cancer can spread to other organs, making treatment increasingly difficult. Therefore, it is very important for us to recognize the causes, symptoms, and prevention methods early on.
Colorectal cancer, which appears as abnormal cell growth in the large intestine or rectum, often begins as polyps—abnormal tissue that grows on the walls of the intestine. While some polyps are benign, there are those that have the potential to become cancerous if left untreated.
The main cause of this transformation is DNA mutations in intestinal cells, leading to uncontrolled cell division and tumor formation. Without symptoms in the early stages, this cancer can develop and invade surrounding tissues, even spreading to other organs.
Therefore, it is important to undergo regular screenings, especially for those at risk, so that polyps can be detected early through procedures such as colonoscopy before they potentially become cancerous.
Colorectal cancer often does not show symptoms in the early stages, especially if it grows on the right side of the large intestine. Watery stools and a larger lumen size can allow tumors to remain hidden for a long time. As a result, many patients only become aware of the cancer when it has already reached an advanced stage.
Here are the symptoms to watch out for:
Continuous changes in bowel habits, especially if they last more than a few weeks, can be an early sign. Both diarrhea and constipation that do not improve should be taken seriously.
Even after having a bowel movement, patients often feel that there is still residue in the intestines. This uncomfortable feeling arises due to a blockage or pressure from a tumor in the intestinal wall.
Blood may be clearly visible or hidden in the form of very dark stools. This can be caused by bleeding from a tumor in the large intestine or rectum.
A growing cancer can cause pressure, cramps, or unusual pain in the abdomen. These symptoms are often misinterpreted as mild digestive disorders.
If you lose significant weight without changing your diet or physical activity, this could be a signal of a serious metabolic disorder, including cancer.
Chronic fatigue occurs because the body is lacking in nutrients and energy due to cancer, especially if accompanied by anemia.
Patients may experience pallor, dizziness, and palpitations due to a lack of red blood cells from chronic bleeding caused by a tumor.
Remember, colorectal cancer usually only causes symptoms when the cancer cells have progressed significantly. This means you should not take lightly complaints that frequently recur, even if they seem trivial.
Colorectal cancer does not appear out of nowhere. There are two main groups of risk factors that influence it: genetic and lifestyle. Although you cannot change hereditary factors, you can still reduce the risk through lifestyle changes.
Here is a complete list of factors that can increase the risk of developing colorectal cancer:
Having parents, siblings, or children who have been diagnosed with colon cancer can significantly increase the risk.
Genetic disorders such as Lynch Syndrome or Familial Adenomatous Polyposis (FAP) can cause the growth of numerous polyps in the large intestine from a young age.
If there is a family member diagnosed with colorectal cancer under the age of 50, screening should be done earlier and more frequently.
A lack of vegetables, fruits, and whole grains can lead to digestive issues and increase the risk of polyp formation in the intestines.
Fast food, fatty red meat, and processed foods contain saturated fats that are closely linked to an increased risk of colorectal cancer.
A sedentary lifestyle or sitting too much without regular exercise contributes to inflammation and poor metabolism in the body.
A high body mass index has been shown to increase the risk of colorectal cancer, as well as decrease the chances of recovery if cancer develops.
Chemicals in cigarettes can damage intestinal cells and trigger DNA mutations that lead to the growth of cancer cells.
Regularly drinking alcohol in large amounts can disrupt hormonal balance and damage the intestinal walls, increasing cancer risk.
Individuals with type 2 diabetes, Crohn's disease, or ulcerative colitis have a higher risk due to long-term inflammation in the digestive tract.
Diagnosis of colorectal cancer involves a series of careful and planned medical steps. The process begins with blood tests to detect possible anemia or elevated CEA levels, which can be early markers of cancer. Next, imaging examinations such as CT scans or MRIs are performed to map the spread of the disease.
However, colonoscopy remains the preferred method for detecting colorectal cancer, as it allows doctors to directly examine the condition of the intestines and perform biopsies if abnormalities are found. Additionally, other procedures such as sigmoidoscopy or proctoscopy may be considered as needed.
This screening is not only aimed at those experiencing symptoms but also at individuals at high risk. Alodokter recommends that everyone over the age of 45 undergo routine screening. Do not hesitate to consult with your doctor about the type and schedule of screening that is most suitable for you.
Although not all cases of colorectal cancer can be prevented, there are several steps that can be taken to reduce the risk:
This information is general and for educational purposes. Always consult with a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment. Symptoms and causes of colorectal cancer can vary, and it is important to seek professional medical care if you experience concerning symptoms.
Colorectal cancer is cancer that develops in the large intestine or rectum, which can be life-threatening if not detected and treated properly.
High-risk individuals include those with a family history of colorectal cancer, those over 50 years old, or those with certain medical conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease.
Screening tests such as colonoscopy are effective methods for early detection of colorectal cancer.
While not all cases can be prevented, adopting a healthy diet, exercising, and undergoing regular screenings can reduce the risk.
(kpl/rmt)
Cobain For You Page (FYP) Yang kamu suka ada di sini,
lihat isinya
In this article, we will discuss the steps to cook rendang so that the meat is tender and the coconut milk remains intact.
Here are the precise steps in cooking opor ayam so that the spices are perfectly absorbed without making the chicken cook too quickly.
One of the biggest challenges when cooking fried liver sambal is eliminating the fishy smell from chicken or beef liver, so that the dish's flavor remains delicious.
Many people experience lontong that is too dense, hard, or even easily crumbles when cut. In fact, with the right technique, lontong can have a perfectly soft and chewy texture.
The F1 film produced by Apple Original Films is set to hit theaters worldwide on June 25, 2025, featuring Brad Pitt, Lewis Hamilton, and other F1 stars!
Tom Holland returns as Spider-Man in 'Spider-Man: Brand New Day', a fresh start without his identity revealed and without the help of the Avengers, releasing on July 31, 2026!
Ma Dong Seok is an outstanding South Korean actor. His diverse roles and exceptional acting skills have captivated millions of viewers around the world.
Get ready to fly! The live-action film How to Train Your Dragon is set to release on June 13, 2025, bringing the adventures of Hiccup and Toothless to the big screen with spectacular visuals.
Peter Parker starts from scratch in SPIDER-MAN 4: BRAND NEW DAY, without the Avengers and a mysterious new enemy threat.
Explore the colorful and dangerous world of Minecraft with Jason Momoa, Emma Myers, and Jack Black in the epic adventure film 'A Minecraft Movie', coming in April 2025!
Cha Eun Woo celebrates his 28th birthday with childhood photos and a princess costume, making fans flood with wishes.
Recognize the signs of healthy kidneys from clear urine to sound sleep, and easy ways to maintain their function.