The Meaning of Ikram According to Primbon: Significance and Its Influence in Life
Learn the meaning of the name Ikram according to Javanese primbon, its noble meaning, and its influence on a person's personality and destiny in life.
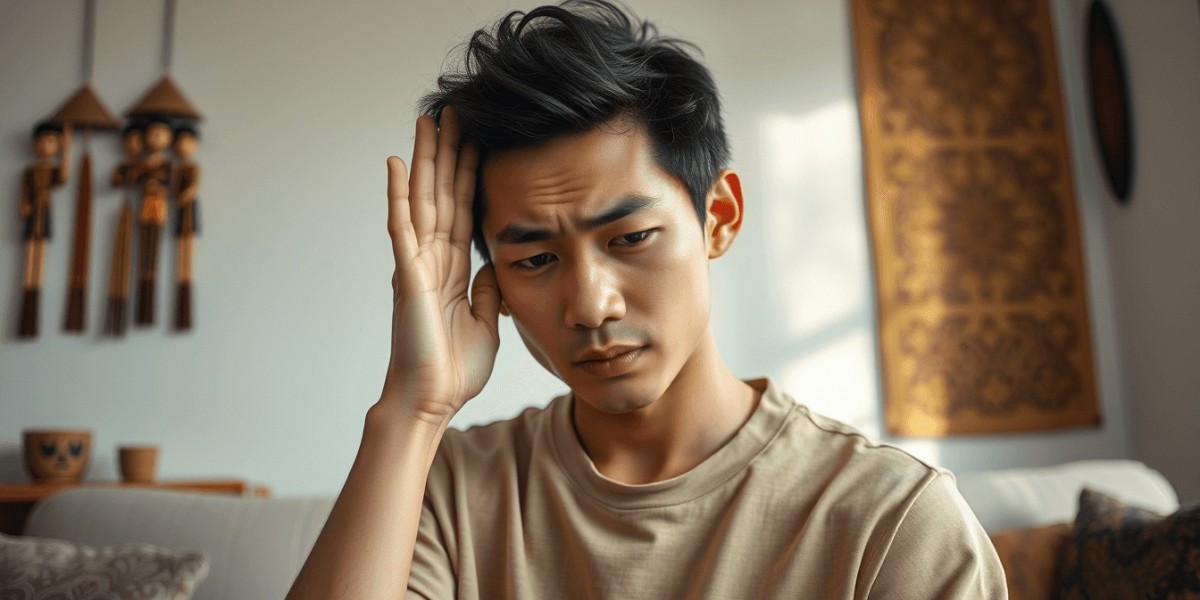

You may have experienced a sudden ringing in your ears without any clear reason. In Javanese culture, this phenomenon is often associated with mystical matters. The meaning of ear ringing in primbon is an interesting topic to explore further.
Many people believe that this ringing is a sign from nature or a supernatural signal. The meaning of ear ringing in primbon provides explanations based on the time and the side of the ear that is ringing. You can also understand the meaning behind this occurrence according to traditional beliefs.

Tinnitus (credit: unsplash)
Tinnitus, or in medical terms referred to as tinnitus, is the sensation of hearing sounds without any actual external sound source. This phenomenon is quite commonly experienced by many people, with estimates suggesting that around 15-20% of the world's population has experienced it at some point. The sounds perceived can be buzzing, hissing, roaring, or other noises that can only be heard by the sufferer.
In the context of Javanese primbon, tinnitus is believed to have its own meaning as a sign or omen of an impending event. This traditional interpretation has become part of the cultural heritage passed down from generation to generation.
Although it lacks scientific basis, the belief in the meaning of tinnitus according to primbon is still held by some members of society. This article will comprehensively discuss the meaning of tinnitus from the perspective of Javanese primbon and provide the latest medical explanations regarding this phenomenon.
In Javanese tradition, ringing in the ears is believed to have different meanings depending on the time it occurs and which ear is ringing. Here are some common interpretations of the meaning of ringing in the ears according to Javanese primbon:
It is important to remember that these interpretations are part of traditional beliefs and do not have a scientific basis. However, for some Javanese people, primbon is still considered a guide in interpreting various events in life.

Tinnitus (credit: unsplash)
From a medical perspective, ringing in the ears or tinnitus is a symptom that can be caused by various health conditions. Below is a scientific explanation regarding the phenomenon of ringing in the ears:
Tinnitus occurs when the hair cells in the cochlea (part of the inner ear) are damaged or irritated. These cells play a crucial role in translating sound waves into electrical signals that are then sent to the brain. When these cells are damaged, they can send random signals to the brain that are interpreted as sound, even though there is no external sound source.
Generally, tinnitus can be divided into two main types:
There are several factors that can cause ringing in the ears, including:
The main symptom of tinnitus is the perception of sound without an external source. The sounds perceived can vary, including:
The intensity of the sound can also vary from mild to very disturbing. Some people may only experience it occasionally, while others experience it continuously.
To diagnose tinnitus, doctors typically take several steps:
Accurate diagnosis is crucial to determine appropriate management. If tinnitus is accompanied by other symptoms such as dizziness, nausea, or balance disturbances, consult a doctor immediately as it may be a sign of a more serious condition.

Tinnitus (credit: unsplash)
Although ringing in the ears or tinnitus is often difficult to completely cure, there are several ways that can help reduce its intensity and improve the quality of life for sufferers. Here are some methods that can be tried:
This therapy involves the use of external sounds to distract from the tinnitus noise. Some options include:
CBT can help change the way one thinks and reacts to tinnitus. This therapy aims to reduce the stress and anxiety that often accompany this condition.
Relaxation methods such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can help reduce tension and improve tolerance to tinnitus.
Although there is no specific cure for tinnitus, some types of medication can help manage accompanying symptoms, such as:
For tinnitus sufferers who also experience hearing loss, the use of hearing aids can help reduce the perception of tinnitus sounds.
This method uses magnetic fields to stimulate nerves in the brain involved in tinnitus. Although still in the research phase, some studies show promising results.
Some lifestyle changes that can help reduce tinnitus include:
Some people report benefits from acupuncture therapy in reducing the intensity of tinnitus, although scientific evidence is still limited.
Protecting the ears from loud sounds can prevent the worsening of tinnitus. Use ear protection when in a noisy environment.
Talking to a mental health professional can help address the emotional impact of tinnitus and improve coping strategies.
It's important to remember that the effectiveness of each method may vary between individuals. Consult an ENT doctor to get a treatment plan that best suits your condition.
As traditional beliefs and medical information evolve, various myths surrounding tinnitus emerge. Let's examine some common myths and their scientific facts:
Fact: Although tinnitus is often associated with hearing disorders, not all cases of tinnitus are caused by or lead to hearing loss. Many people with tinnitus have normal hearing.
Fact: Although there is currently no cure that can completely eliminate tinnitus, there are various treatment and management methods that can help reduce its intensity and improve the quality of life for sufferers.
Fact: Tinnitus can affect people of all ages, including children and teenagers. Risk factors do increase with age, but it is not exclusive to the elderly.
Fact: Not always. Many people report that the intensity of their tinnitus remains stable or even improves over time, especially with proper management.
Fact: Although exposure to loud sounds can trigger tinnitus, it is often temporary. However, repeated and prolonged exposure can indeed increase the risk of permanent tinnitus.

Tinnitus (credit: unsplash)
Although ringing in the ears or tinnitus is often not a serious condition, there are several situations where you should consult a doctor immediately. Here are some signs that indicate you should seek medical help:
If you experience ringing in the ears that appears suddenly and is very disturbing, contact a doctor immediately. This could be a sign of a problem that requires urgent attention.
The combination of ringing in the ears with severe dizziness or vertigo (a spinning sensation) can indicate a disturbance in the balance system in the inner ear.
If you experience tinnitus that occurs only in one ear, especially if accompanied by hearing loss, this could be a sign of a tumor or other issues that require further evaluation.
Tinnitus that sounds like a pulsing, especially if it is in sync with your heartbeat, could indicate a problem with the blood vessels around the ear.
If your ears are ringing accompanied by pain or discharge from the ear, this could be a sign of an infection that requires medical attention.
If tinnitus is so disruptive that you have difficulty sleeping or cannot concentrate on daily activities, consult a doctor for appropriate management strategies.
If you feel your hearing is declining along with the onset of tinnitus, see an ENT doctor immediately.
Although ringing in the ears or tinnitus is often considered a minor disorder, its impact on the daily lives of sufferers can be quite significant. Here are some aspects of life that can be affected by tinnitus:
One of the most common impacts of tinnitus is sleep disturbance. Many sufferers report difficulty falling asleep or often waking up in the middle of the night due to the ringing sounds they experience. Lack of quality sleep can lead to fatigue, irritability, and decreased cognitive function during the day.
Tinnitus can severely disrupt a person's ability to concentrate on tasks that require high focus. This can significantly impact productivity at work or the ability to learn for students.
Tinnitus can affect a person's ability to fully participate in conversations, especially in noisy environments. This can lead to feelings of frustration and social isolation. Some sufferers may avoid certain social situations due to concerns about not being able to hear clearly or feeling disturbed by their tinnitus sounds.
Living with chronic tinnitus can significantly impact a person's mental health. Many sufferers report feelings of anxiety, depression, or increased stress as a result of this condition. The frustration of being unable to "escape" the sound of tinnitus can lead to mood and behavioral changes that affect personal and professional relationships.
Tinnitus can affect a person's ability to enjoy certain hobbies or recreational activities. For example, a musician may have difficulty hearing notes clearly, or someone who enjoys the tranquility of nature may feel disturbed by the sound of tinnitus while camping or hiking.

Tinnitus (credit: unsplash)
Although tinnitus has long been the subject of medical research, recent years have witnessed promising developments in the understanding and management of this condition. Here are some recent research areas that offer new hope for tinnitus sufferers:
Recent research in the field of gene therapy shows promising potential for addressing tinnitus caused by damage to the hair cells in the inner ear. Scientists are developing methods to replace or repair the damaged genes responsible for the production and function of these hair cells.
Non-invasive brain stimulation techniques, such as Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) and transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS), are being investigated as potential treatments for tinnitus. These methods aim to modulate nerve activity in the brain areas associated with the perception of tinnitus sounds.
The development of smartphone applications and specialized devices that provide personalized sound therapy for each individual is becoming a focus of research. This technology uses advanced algorithms to analyze a person's tinnitus characteristics and generate the most effective therapeutic sounds for them.
Neurofeedback techniques, which involve training the brain to change its neural activity patterns, are being explored as a potential method for managing tinnitus. Early research suggests that by training the brain to alter its response to tinnitus signals, some sufferers may experience a reduction in the intensity of their symptoms.
Researchers continue to seek new medications that can help manage tinnitus. Some focus areas include the development of drugs targeting specific neurotransmitters in the brain associated with sound perception, as well as medications that can protect nerve cells from further damage.
Although tinnitus is often associated with adults and the elderly, this condition can also affect children and teenagers. However, tinnitus in younger age groups is often underdiagnosed or misunderstood. Here are some important aspects regarding tinnitus in children and teenagers:
Studies show that tinnitus in children and teenagers is more common than previously estimated. However, because children may have difficulty describing or communicating what they are experiencing, this condition is often undetected. Symptoms of tinnitus in children can vary, ranging from buzzing or hissing sounds to a constant high-pitched tone.
The causes of tinnitus in children and teenagers may differ from those in adults. Some contributing factors include:
Tinnitus can have a significant impact on a child's ability to learn and concentrate in school. It can affect their academic performance and social development. Children with tinnitus may have difficulty hearing teacher instructions, participating in class discussions, or interacting with peers.
Diagnosing tinnitus in children requires a different approach than in adults. Doctors may need to use communication methods tailored to the child's age and involve parents or guardians in the diagnostic process. Comprehensive hearing examinations and thorough medical evaluations are crucial for identifying underlying causes and planning appropriate treatment.
Tinnitus (credit: unsplash)
Tinnitus or ringing in the ears is a complex phenomenon with various interpretations, both from traditional perspectives such as Javanese primbon and modern medical viewpoints. While primbon offers intriguing interpretations of the meaning of ringing ears, it is important to understand that there is no scientific basis supporting these claims.
From a medical standpoint, tinnitus is a symptom that can be caused by various factors, ranging from exposure to loud sounds to more serious health conditions. Although often not harmful, tinnitus can significantly impact a person's quality of life, affecting sleep, concentration, and mental health.
Managing tinnitus requires a comprehensive approach, involving medical evaluation, sound therapy, and in some cases, psychological support. Developments in medical research continue to pave the way for more effective treatment methods in the future.
For those experiencing persistent ringing in the ears, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management. Meanwhile, understanding and appreciating cultural interpretations can provide interesting perspectives, but should not replace necessary medical care.
With a better understanding of tinnitus, both medically and culturally, we can manage this condition more effectively and improve the quality of life for those affected.
Discover more interesting reviews at kapanlagi.com. If not now, when?
(kpl/psp)
Cobain For You Page (FYP) Yang kamu suka ada di sini,
lihat isinya
Learn the meaning of the name Ikram according to Javanese primbon, its noble meaning, and its influence on a person's personality and destiny in life.
Here is a complete review of Claude AI, from its definition, features, to how to log in and use this platform easily and practically.
Learn the meaning and philosophy behind the primbon belief about husbands punished by their wives. Discover the significance, traditions, and modern perspectives related to this.
Learn the meaning of the name Adi according to Javanese primbon along with its philosophical meaning, characteristics, and influence. A complete guide to choosing a name with a good meaning.
Learn about the myths and facts surrounding the phenomenon of babies growing hair on their buttocks according to Javanese primbon. Check out the medical explanations and traditional beliefs related to this.
Learn how to find your Javanese primbon weton easily and accurately. Discover the meaning behind your weton and its benefits in daily life.
Explore the deep meaning behind dreaming of the adhan according to Javanese primbon. Discover the interpretations and spiritual insights from this dream experience.
Have you ever experienced left eye twitching? Check out the complete explanation of the meaning of left eye twitching according to Javanese primbon along with the medical perspective here.
Explore the deep meaning behind dreams of clothes floating in the river according to Javanese primbon. Discover the interpretation and symbolism of this unique dream experience.
For those of you who want to watch an anime with a love polygon among siblings. Here is the complete synopsis of SHIUNJI KE NO KODOMO TACHI anime 2025 that is a must-watch. Let's check it out, KLovers!
One of the latest releases that you should watch is NOCTURNAL (2025). This latest film by Kim Nam Gil, which premiered in early 2025, presents a combination of psychological tension, mystery, and family intrigue that binds emotions.
How to watch Filipino movies on legal sites available in Indonesia. Let's check out the legal ways to watch Filipino movies below!